September 20, 2024 /SemiMedia/ — South Korea is accelerating the development of its high-bandwidth memory (HBM) supply chain, critical for AI computing, while Japanese chip equipment makers are securing supply agreements with industry leaders.
Tokyo Electron (TEL), Japan’s largest semiconductor equipment manufacturer, is building its fourth R&D center in Yongin, near Seoul, slated to open in 2026. The facility will focus on customer prototype design, underscoring the importance of development speed.
The Yongin semiconductor cluster is expected to open in 2027, with major investments from SK Hynix and Samsung Electronics to produce HBM. Over the past five years, TEL Korea has doubled its workforce, focusing on equipment maintenance engineers.
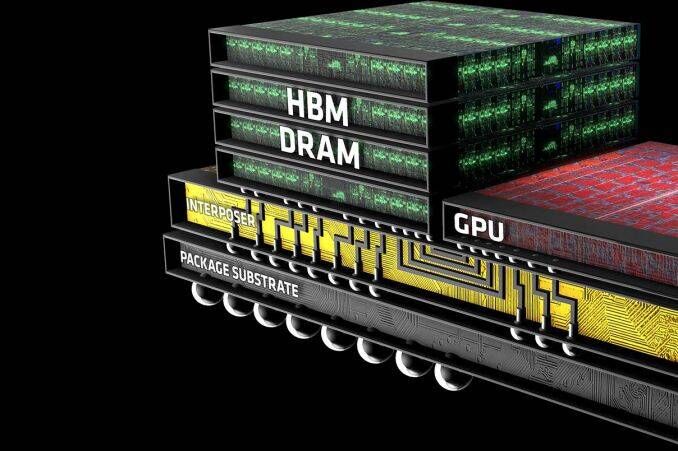
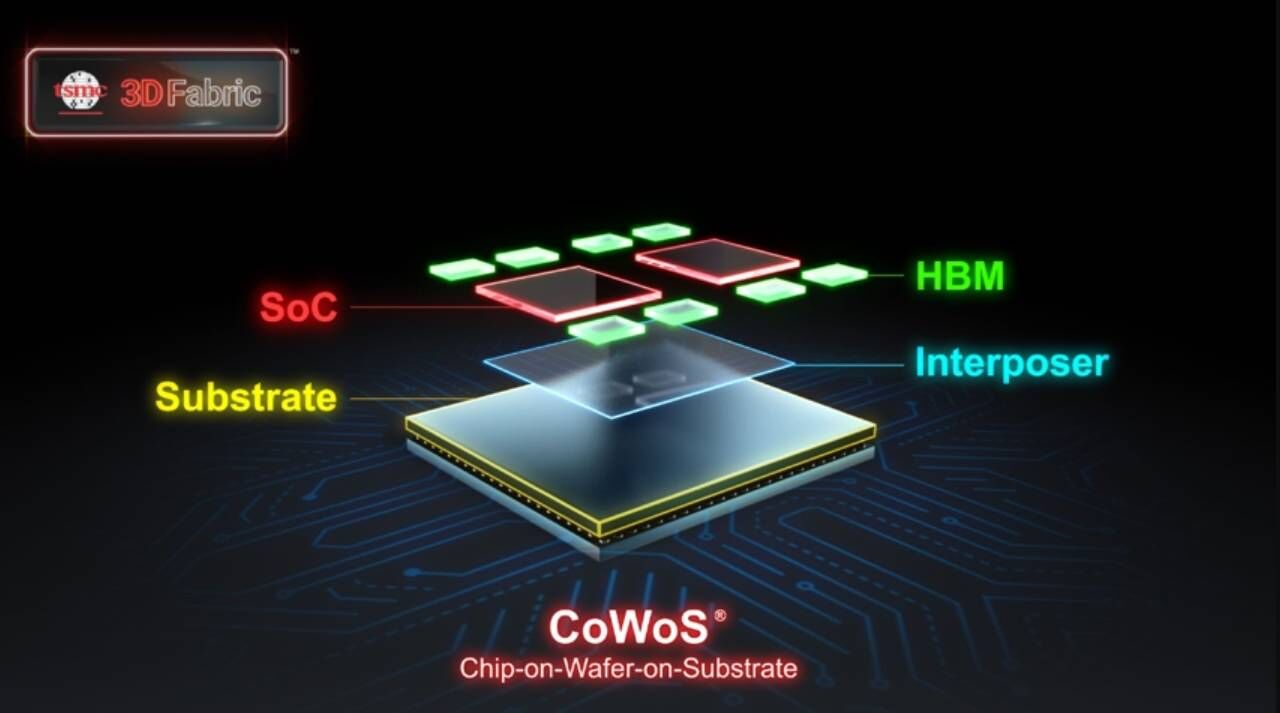
HBM’s demand is driven by AI servers due to its high performance and low power consumption. The global HBM market is projected to grow sixfold by 2027, reaching $17.5 billion. SK Hynix currently holds around 50% of the market, followed by Samsung Electronics with 40%.
Another Japanese supplier, Towa, plans to open a molding equipment factory in Cheonan by 2025, its largest project in Korea. This facility is expected to double sales and capacity once operational.
South Korea's local semiconductor equipment supply is limited, covering only about 20% of demand. To boost domestic production, the government has designated HBM as a strategic technology, offering tax incentives and tripling subsidies for foreign manufacturers by 2024.
With relations between South Korea and Japan improving, Japanese firms see fewer barriers to investment. This trend is expected to further solidify South Korea's position as a key player in the global HBM market.









All Comments (0)